
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, a substance use disorder (SUD) is a mental disorder that affects a person’s brain and behavior, leading to a person’s inability to control their use of substances such as legal or illegal drugs, alcohol, or medications.
The diagnosis of SUD is based on the pathological pattern of behaviors set in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-V). SUDs are divided into two groups: substance use disorder and substance-induced disorders.
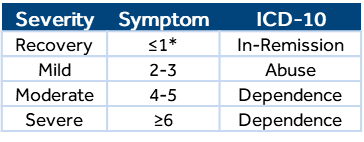
Substance-induced disorders generally occur during the intoxication and withdrawal period. Coders cannot assume a relationship between a SUD under the “with” guideline. Documentation must indicate a cause-and-effect relationship. Patients who have recovered from a SUD should be coded as “in-remission;” however, these patients may still experience cravings.*
When patients are prescribed a drug and are taking it under appropriate medical supervision, the DSM-V criteria excludes Criteria 10-11.* However, prescriptions can be used inappropriately and a SUD can be diagnosed when there are other symptoms of compulsive, drug- seeking behavior.
When patients are taking an opiate, as prescribed for pain management, the correct code is Z79.891 Long term (current) use of opiate analgesic.
When the provider refers to use, abuse, and dependence of the same substance (i.e., alcohol, opioid, cannabis, etc.), only one code should be assigned to identify the pattern of use.
- If use and abuse: assign only abuse
- If use, abuse, and dependence: assign only dependence
DSM-V Diagnostic Criteria
Criterion (1-4): Impaired Control Over Substance Use
- Taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than was intended
- Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control substance use
- A great deal of time is spent in activities necessary to obtain and use the substance, or recover from it
- Craving, or a strong desire or urge to use substance
Criterion (5-7): Social Impairment
- Recurrent substance use resulting in a failure to fulfill major obligations at work, school, or home
- Continued substance use despite having persistent or recurrent social or interpersonal problems caused or exacerbated by the effects of substance
- Important social, occupational, or recreational activities are given up or reduced because of use
Criterion (8-9): Risky Use of Substance
- Recurrent opioid use in situations in which it is physically hazardous
- Continued opioid use despite knowledge of having a persistent or recurrent physical or psychological problem that is likely to have been caused or exacerbated by the substance
Criterion (10-11): Pharmacological Criteria*
- Tolerance, as defined by either of the following:
- A need for markedly increased amounts of substance to achieve intoxication or desired effect
- A markedly diminished effect with continued use of the same amount of a substance
- Withdrawal, as manifested by either:
- Characteristics of substance withdrawal syndrome
- Substances are taken to relieve or avoid withdrawal symptoms
RESOURCES: ICD-10-CM Guidelines; NIH; AHA 2022 Q1 pg.34; DSM-V
ADDITIONAL CASE STUDY: https://www.chesshealthsolutions.com/2021/03/12/hcc-coding-identifying-and-correctly-documenting-alcohol-use-disorders/
About the Author


