Much has been said about health equity in value-based care. Indeed, health equity is now frequently referred to as a key component of the fifth element of a Quintuple Aim to lead healthcare improvement and for success in value-based care.
Don Berwick, John Whittington, and Tom Nolan first described the Triple Aim for Healthcare Improvement in 2008. Its goal is to define the role of health care in society. These goals include increasing population health, enhancing the care experience for individuals, and lowering the per capita cost of care.
In 2014, it was decided that adding another element – taking care of the requirements of the healthcare provider – was necessary. The Quadruple Aim for healthcare improvement was created as a result. As the healthcare sector started to address healthcare worker burnout by addressing excessive performance demands and cognitive load, this new component came into sharper emphasis.
The Quintuple Aim is an extension of the Quadruple Aim, adding an additional dimension to the healthcare framework. It emphasizes the importance of optimizing the overall healthcare system to establish health equity. In the context of value-based care, the Quintuple Aim becomes even more critical as it aligns with the core principles and goals of value-based care models.
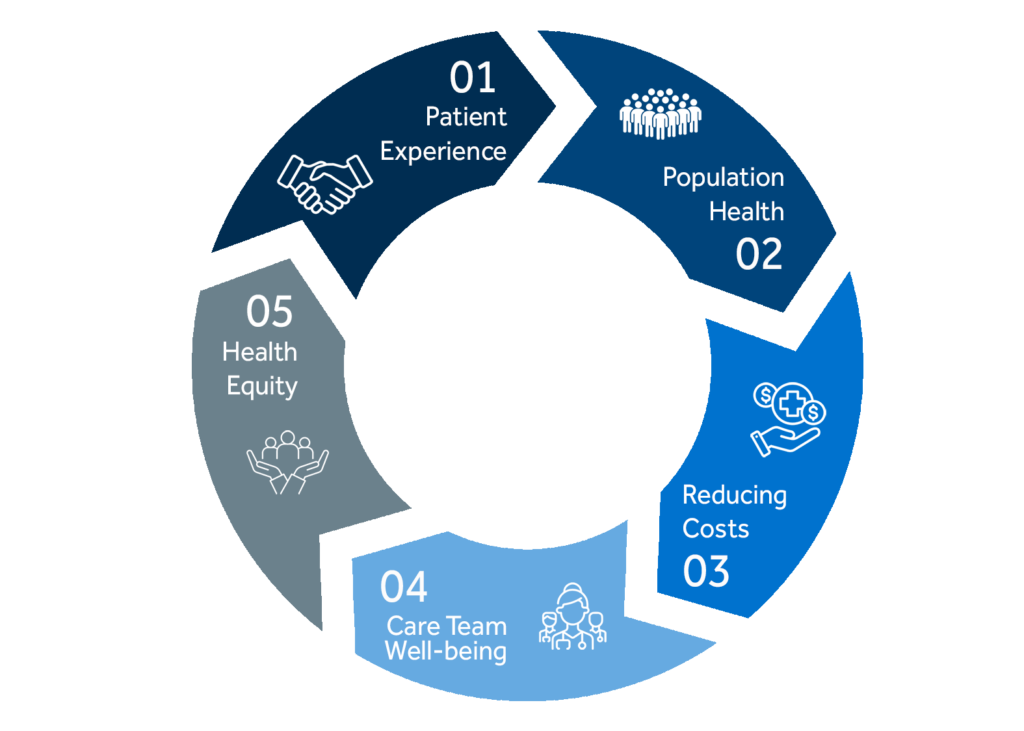
Here’s why the quintuple aim is essential in value-based care:
Patient-Centered Care
Value-based care improves patient outcomes and experiences by providing patient-centered care. The Quintuple Aim supports this goal by emphasizing the importance of enhancing the patient experience, fostering trust, communication, and engagement between patients and healthcare providers. By putting patients at the center of care, value-based care models can tailor treatments and interventions to individual needs, leading to better health outcomes.
Population Health Management
Value-based care goes beyond individual patient care and focuses on improving the health of entire populations. The Quintuple Aim aligns with this objective by recognizing the significance of addressing social determinants of health and implementing preventive measures to promote wellness within communities. By managing population health effectively, value-based care models can reduce the burden of chronic diseases and improve overall community well-being.
Cost Efficiency
One of the primary goals of value-based care is to control healthcare costs while maintaining high-quality care. The Quintuple Aim’s “Reduce Costs” dimension complements this goal by encouraging healthcare organizations to identify areas of inefficiency, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation. This ensures the cost savings achieved through value-based care can be invested in improving patient care and outcomes.
Provider Well-being and Engagement
Value-based care models can lead to increased administrative burdens and performance pressure on healthcare providers. The Quintuple Aim’s focus on “Improve Provider Well-being” is crucial in this context, as it recognizes that healthcare professionals’ satisfaction and engagement are essential for delivering high-quality care. When providers are supported, and their well-being is prioritized, they are more likely to be motivated and dedicated to providing patient-centered care.
Enhance Care Team Satisfaction and Collaboration
Health equity in value-based care involves fostering a collaborative and inclusive care team environment. When care teams work together to address health disparities and provide equitable care, patient outcomes and team satisfaction can improve. Furthermore, recognizing the impact of social determinants of health on patients’ well-being can enhance communication and collaboration among care team members, enabling them to develop comprehensive care plans that consider the unique needs of each patient.
By integrating health equity into the Quintuple Aim, value-based care models can work towards creating a more just and equitable healthcare system. Health equity improves the overall health of populations, enhances patient experiences, promotes provider well-being, and ensures all members of the community have an equal opportunity to access high-quality healthcare services. Health equity is not only an ethical imperative but also a critical factor in achieving better health outcomes and a more sustainable healthcare system.
By addressing all five dimensions of the Quintuple Aim, value-based care models can create a more sustainable healthcare system. When patient outcomes improve, population health is managed effectively, costs are controlled, providers are engaged, and care teams collaborate efficiently, the healthcare system becomes more resilient and better equipped to meet the needs of the population over the long term.
About the Author


