
Dementia is a progressive decline in cognition, both long- and short-term memory loss, which can be due to a disease or brain damage. Dementia can be a direct result of an underlying condition or a substance that is being used. Dementia can be described as “due to” multiple conditions or can be inherit to others. Common underlying etiologies are listed below:
- Alzheimer’s
- Parkinson’s
- Lewy Body
- Traumatic Brain Injuries
- Alcohol and Drug Induced
- Vascular/Stroke
In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition (DSM-V), the presence or absence of a behavioral disturbance is a criterion for dementia patients. Mood disturbances, agitation, apathy, violence, aggression, and uncooperative behaviors are considered behavioral disturbances.
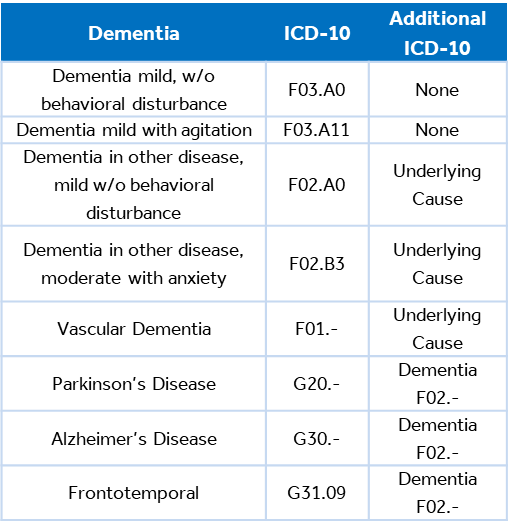
There are certain documentation elements required to appropriately support and communicate the quality of care delivered for patients diagnosed with dementia. In most forms of dementia, one code will describe the etiology and a second code will describe dementia.
Dementia should be documented for all encounters where it impacts care planning. Documentation should include describing the patient’s mental capabilities, symptoms, or diagnosis, including wandering or sundowning.
In 2022, the ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes were updated for dementia to include specificity regarding the severity and type of mood disorders present.
The Alzheimer’s Association has created a screening tool to assist providers with assessing the severity of dementia in their patients. This tool is known as the Dementia Severity Rating Scale (DSRS).
Documentation & Coding
When documenting dementia, it is important to limit the use of abbreviates, link the underlying cause to dementia, describe it as current vs. historical, and provide a final assessment of the condition.
- Limit or avoid abbreviations
- Specify severity as Mild, Moderate, Severe
- Do not describe current dementia as a “history of.” In diagnosis coding, the phrase “history of” indicates the condition no longer exists
- Most dementia conditions require two ICD-10-CM codes to fully describe the etiology, severity, and mood disorders present
- Use additional code, if applicable, to identify wandering Z91.83
SOURCES: DSRS Tool; FY24 ICD-10 Guidelines;

