
What is Patient-Centered Care?
Patient-centered care (PCC) is a healthcare model that considers not just a patient’s symptoms and medical history, but also their emotional, social, financial circumstances, and values. This approach is often seen as a collaborative partnership between the patient and healthcare provider, where the patient’s perspective is given equal importance to that of the doctor or nurse.
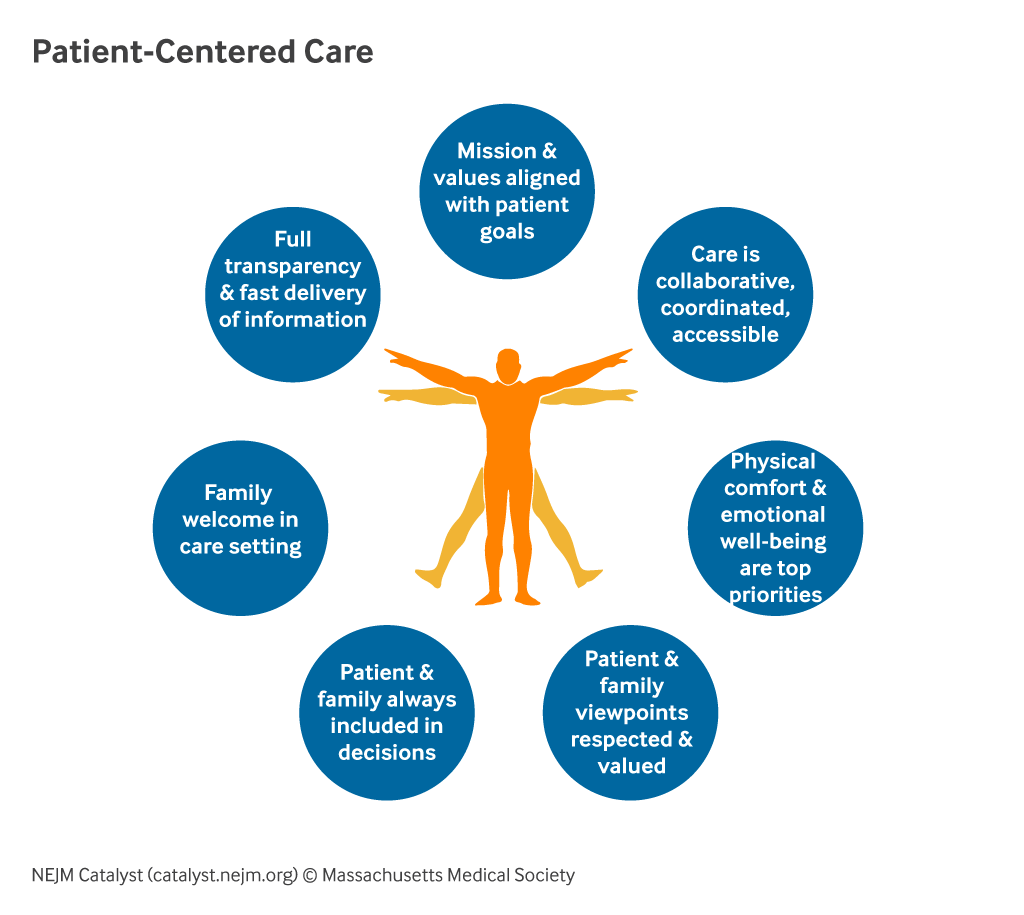
Principles of Patient-Centered Care
The goal of patient-centered care is to empower patients to become active participants in their health journey, improving individual health outcomes. At its core, PCC revolves around placing the patient at the center of the healthcare experience. It encompasses several key principles:
- Respect for Patient Values and Preferences: Healthcare decisions should be guided by the individual needs, values, and preferences of each patient. This requires active communication and collaboration between patients, their families, and healthcare providers.
- Coordination of Care: A patient-centric approach emphasizes the importance of coordinating and integrating all aspects of healthcare, including preventive, acute, and chronic care, to ensure seamless transitions and continuity of care.
- Information and Education: To enable informed decision-making, patients should be provided with information that is accurate, accessible, and actionable.
- Physical Comfort and Emotional Well-being: Patients’ physical comfort and emotional well-being should be considered. Healthcare providers should offer empathetic and compassionate support.
- Family and Caretaker Involvement and Support: Partner with patients and families, welcome their involvement, and personalize care.
Benefits of Patient Centered Care
Patient: A patient centered model helps patients feel heard. It shifts the traditional role of a patient from an “order taker” to an active “team member.” Studies show that patients who receive patient-centric care tend to have better health outcomes than those who do not.
Provider: Patient centered care benefits healthcare providers by allowing them to spend more time with patients, getting back to practicing medicine. When patients are at the center of care, providers can facilitate more individualized care plans that benefit practitioners and patients.
Health System: A patient centered model benefits the whole health system by improving resource allocation and reducing costs. It also boosts morale and productivity among clinicians and ancillary staff.
Implementing PCC in Value-Based Models
To effectively implement PCC within value-based care, healthcare organizations should consider the following strategies:
- Empowering Patients: Provide patients with the information, tools, and support they need to actively participate in their care.
- Promoting Care Coordination: Implement processes and technologies that facilitate communication and coordination among healthcare providers to ensure seamless transitions and continuity of care.
- Training and Education: Educate providers on the principles of PCC and provide ongoing training to enhance their communication and interpersonal skills.
- Measuring and Monitoring Outcomes: Establish metrics to assess the impact of patient-centric care on health outcomes, patient satisfaction, and healthcare costs.
Patient-centered care is not just a buzzword; it is a fundamental approach to healthcare that aligns with the goals of value-based care. By prioritizing individual needs and preferences, providers can improve outcomes, enhance patient satisfaction, and reduce costs. As healthcare systems evolve, embracing patient centered care will be essential in delivering high-quality, cost-effective care.
RESOURCES: AHRQ Patient-Centered Healthcare, CMS Person Centered Care, NEJM Catalyst

