For Medicaid beneficiaries, especially those with limited resources and complex health conditions, a robust Initial Health Risk Assessment (IHRA) is crucial. This assessment is a gateway to understanding an individual’s needs and potential risk factors, offering a roadmap for personalized care and targeted social interventions.
What is an Initial Health Risk Assessment?
An IHRA helps care managers identify and address unmet health-related resource needs, also known as social determinants of health. These non-clinical barriers to health, such as food insecurity and housing instability, drive up to 70% of a person’s overall health.
The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services (NCDHHS) identified the necessity of addressing these unmet resource needs to improve the health of North Carolinians and implemented a set of standardized SDOH screening questions for Medicaid beneficiaries. PHPs are required to embed these questions into their Care Needs Screening instruments, which is the first step in the care management process.
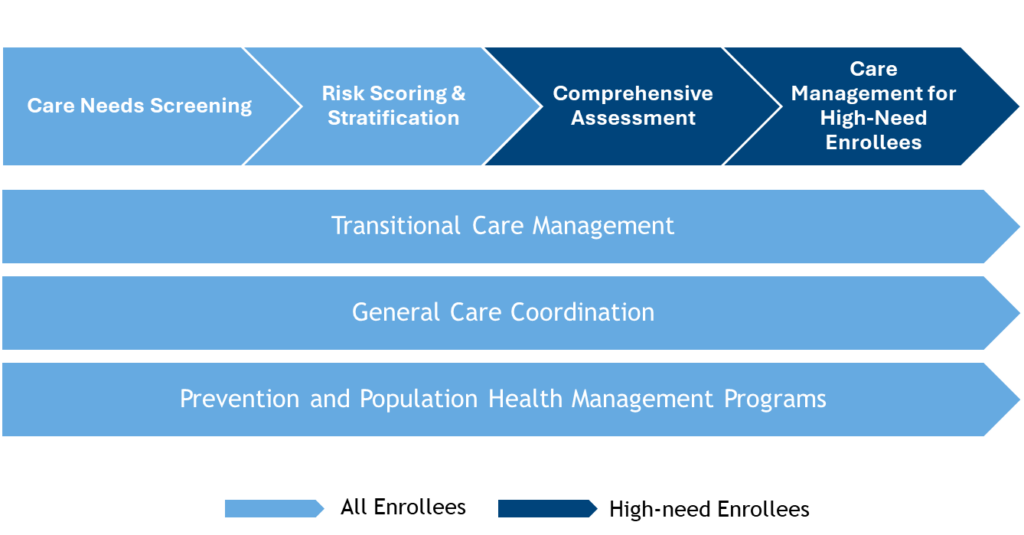
The SDOH screening tool includes questions surrounding food, housing/utilities, transportation, and interpersonal safety. It also includes an optional question about immediate needs.
Benefits of an Initial Health Risk Assessment
- Enhanced Care Coordination: By systematically assessing members’ needs, care managers can better coordinate care, ensuring all aspects of a member’s health are addressed. This coordinate approach also strengthens the relationship between the care team and patient.
- Data-Driven Approach: The data collected from this screening can be used to improve services and address gaps in care. A standardized approach also helps health-related resource needs be proactively addressed, rather than waiting for these issues to surface in later conversations.
- Early Identification & Intervention: Early identification of SDoH results in timely interventions and better health outcomes.
- Increased Patient Engagement: When patients see their social needs being considered, they are more likely to engage in their care plans. This engagement can lead to better health outcomes and a more collaborative relationship.
- Trust & Relationship Building: The IHRA often kicks off a patient’s relationship with a care manager. By starting the interaction with “what can we do to help,” rather than “you should do this,” patients tend to be more open with and trusting of their care manager.
The significance of the Initial Health Risk Assessment for Medicaid beneficiaries cannot be overstated. It is a powerful mechanism for building stronger, more trusting relationships between patients and care team members. By identifying and addressing social determinants of health early, IHRAs lay the groundwork for fostering open communication, enhancing patient engagement, improving care coordination, and ultimately contributing to better health outcomes for Medicaid populations.
RESOURCES: NCDHHS Healthy Opportunities Screening Questions
About the Author


