
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is a common condition that affects the body’s arteries. Healthy lifestyle habits such as not smoking, exercising, and eating well can help prevent and treat high blood pressure.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there is an estimated 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 years old worldwide who have hypertension. Approximately 46% of adults with hypertension are unaware that they have this condition.
Untreated high blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other serious health problems. The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association divides blood pressure into four general categories:
- Normal Blood Pressure ≤ 120/80
- Elevated Blood Pressure 120-129/<80
- Stage 1 Hypertension 130-139/80-89
- Stage 2 Hypertension ≥140/≥90
Blood pressure higher than 180/120 is considered a hypertensive emergency or crisis.
Controlling Blood Pressure (CBP) is a quality measure for many health plans. Healthcare providers and plans can help individuals manage their high blood pressure by prescribing medications and encouraging low-sodium diets, increased physical activity, and smoking cessation. Blood pressure readings are reported to the health plan utilizing the following CPT-II reporting codes:
Systolic
- 3074F Most recent systolic blood pressure < 130
- 3075F Most recent systolic blood pressure 130-139
- 3077F Most recent systolic blood pressure ≥ 140
Diastolic
- 3078F Most recent diastolic blood pressure < 80
- 3079F Most recent diastolic blood pressure 80-89
- 3080F Most recent diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90
Documentation & Coding
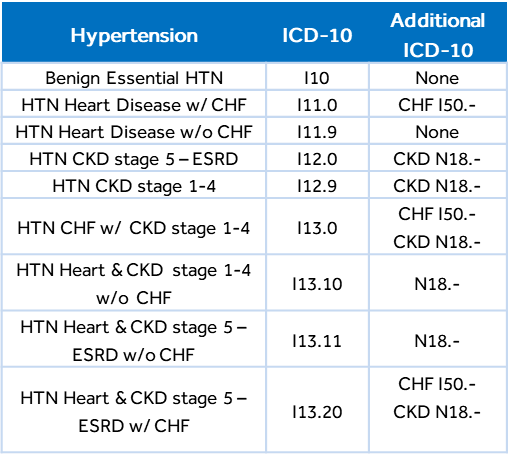
ICD-10-CM presumes a cause-and-effect relationship between hypertension (HTN), heart disease, and chronic kidney disease. These conditions should be coded as related even in the absence of physician documentation explicitly linking them unless the documentation clearly states the conditions are unrelated.
Clarity is important when documenting hypertension. Ensure the diagnosis is captured by noting it in the medical record documentation:
- Primary or secondary hypertension
- Smoking status of the patient
- Relationship between retinopathy, CHF, CKD, etc.
Categories I10-I13 classify primary hypertension according to a hierarchy of the disease from its vascular origin (I10) to the involvement of the heart (I11), CKD (I12), or heart and CKD combined (I13).
RESOURCES: WHO; ICD-10-CM Guidelines
About the Author


